

Hotline:0755-22277778
Tel:0755-22277778
Mobile:13826586185(Mr.Duan)
Fax:0755-22277776
E-mail:duanlian@xianjinyuan.cn
1、 Case background
| problem input |
① An electric taxi equipped with a pricing system from a certain company shows messages such as "network communication failure" and "charging prohibited, please check the smart terminal" on the dashboard when it is powered on again after parking; ② Taxis without installed meter systems have never experienced the above-mentioned fault prompts; |
| On site investigation |
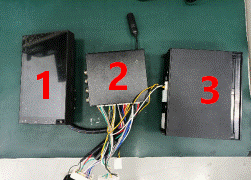
The meter system mainly includes terminal host, meter, etc. Its communication and power supply methods are as follows: ① The communication method adopts CAN network to communicate with the onboard TBOX and gateway; ② The vehicle's 12V battery provides power to both the terminal host and the meter, while the terminal host supplies power to the central control screen through a low-voltage harness; |
| Serial Number |
name |
| 1 |
Central control screen |
| 2 |
Terminal host |
| 3 |
meter |
2、 Data analysis
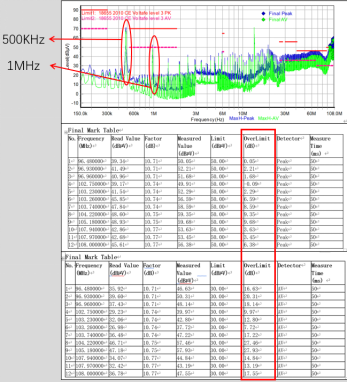
EMC testing was conducted on the pricing system using professional equipment and in accordance with the testing standards specified in GB/T 18655-2010. The test results are shown in the figure on the right;
According to the test results, it can be found that the overall electromagnetic noise of the system is poor, with severe exceedances of around 1M and between 30M and 108M. As shown in the red box on the right, a portion has been extracted
Excessive frequency points; In the frequency range of 150K~108M, it can be clearly seen that the frequency point around 500K has been reached
Up to 70dB; Although this frequency point is not within the frequency range specified in GB/T 18655-2010, its significant electromagnetic noise can affect other frequency points through frequency doubling. According to the test results, it can be seen that the trend of electromagnetic noise in the frequency range of 150K~108M is exactly the same as that of noise around 500K, and the electromagnetic noise at the frequency point exceeding the standard around 1M is most similar to that at the frequency point around 500K. Through analysis, it can be inferred that the noise at the 500K frequency is the fundamental frequency, and subsequent noise is generated by its harmonics; Therefore, reducing the noise at the 500K frequency point is crucial. Because the taxi meter system is not an isolated component (mainly including the meter and terminal host), before conducting EMC rectification and optimization, it is necessary to determine which electromagnetic noise is generated by the meter and which electromagnetic noise is generated by the terminal host in the 150K~108M frequency band.
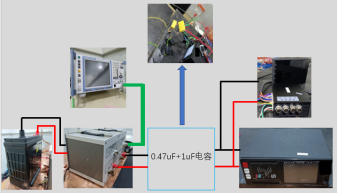
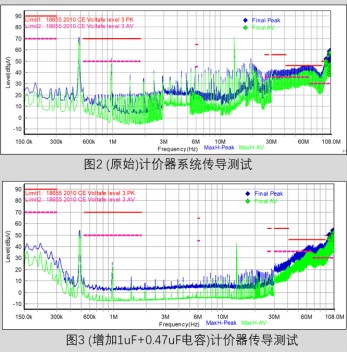
Comparing the test results of Figure 2 and Figure 3, it can be clearly observed that the frequency range from 150K to 60M has significantly decreased, the frequency range around 500K has decreased by nearly 20dB, the frequency range around 1M and the frequency range between 26M and 60M also meet the standard requirements, and the margin is above 6dB. But there was no significant change within the range of 60M~108M.
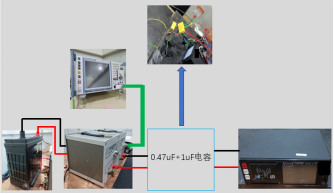
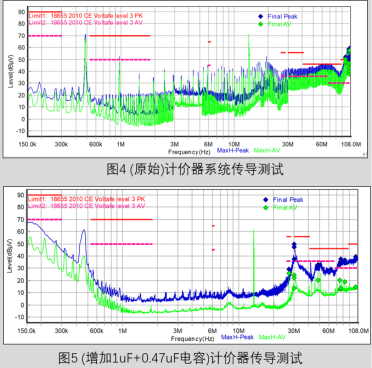
Disconnect the power supply to the terminal host and central control screen, and test the meter separately. The results are shown in Figure 5; It can be clearly seen that the exceeding points within the range of 60M~108M have disappeared, and it can be inferred that the electromagnetic noise within the range of 60M~108M mainly comes from the terminal host and the central control screen; The electromagnetic noise within the range of 150K~60M mainly comes from the meter.
3、 Rectification case
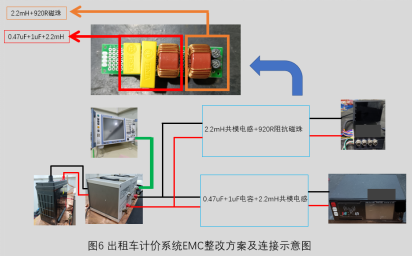
| Rectification measures |
role |
| Add 0.47uF capacitor, 1uF capacitor, 2.2mH common mode inductor at the power supply port of the taxi meter |
① A 0.47uF capacitor and a 1uF capacitor have a significant suppression effect on electromagnetic noise in the frequency range of 150K~60M; ② Connect a 2.2mH common mode inductor in series with the back end of the capacitor to further eliminate electromagnetic noise between 30M and 60M; |
| Add 2.2mH common mode inductor 920R magnetic beads at the power supply port of the taxi terminal host |
① The high-frequency noise between 60M and 108M comes from the terminal host and the main control screen; Therefore, a 2.2mH common mode inductor is connected in series at its power supply port to suppress electromagnetic noise within this frequency range; ② Due to the process conditions and inherent characteristics of common mode inductance winding, leakage inductance exists. Therefore, 920R magnetic beads are connected in series at the back end to offset the impact of common mode inductance leakage inductance; |
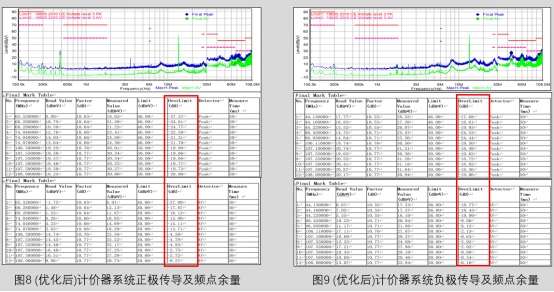
4、 Summary
Summary of the plan and follow-up situation:
① This solution measures are added to the external wiring harness of the taxi pricing system, therefore ranging from 100M to 108M
The margin of the internal frequency division points within the frequency range is less than 6dB; If placed at the component port or directly welded to the outlet
The effect will be more pronounced on the internal PCB circuit boards of each component of the car rental pricing system;
② This plan has been adopted by the taxi pricing system supplier for product optimization and upgrading;
EMC Rectification Tips:
1、 Differential mode interference and common mode interference
Differential mode interference: It exists between the L-N lines, where current enters from L, flows through the positive terminal of the rectifier diode, then through the load, passes through the thermal ground, reaches the rectifier diode, and then returns to N. On this path, there are high-power devices with high-speed switches and diodes with extremely short reverse recovery time. The high-frequency interference generated by these devices will flow through the entire circuit and be detected by the receiver, resulting in conduction exceeding the standard.
Common mode interference: Common mode interference is caused by parasitic capacitance between the ground and the equipment cable. High frequency interference noise will pass through this parasitic capacitance, generating common mode current between the ground and the cable, resulting in common mode interference.
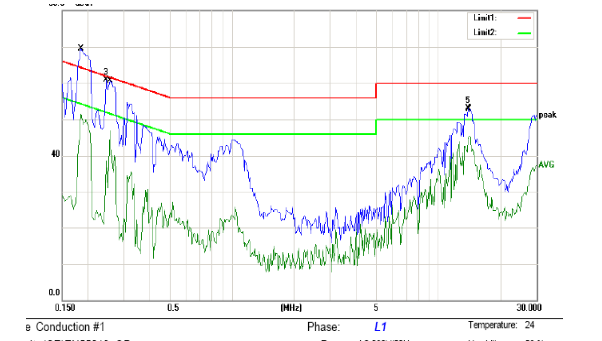
The following figure shows the conducted FALL data caused by differential mode interference. The front-end of the test data exceeds the standard, which is caused by differential mode interference:
The following figure shows the EMI principle of switch mode power supply:
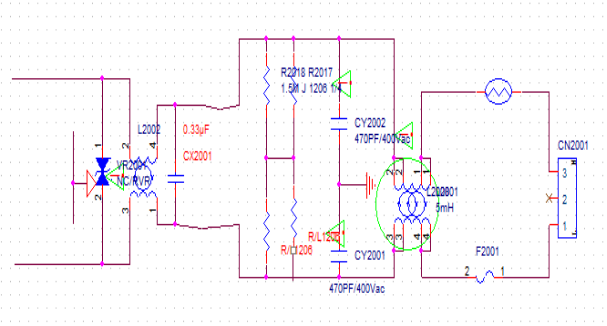
In the figure, CX2001 is a safety film capacitor (which appears as an open circuit when the capacitor is broken down or damaged). It spans between the L and N lines, and when the current between L-N flows through the load, it will bring high-frequency noise into the circuit. At this point, the function of the X capacitor is to form a circuit between the load and the X capacitor, allowing the high-frequency current to be diverted and consumed in the circuit without entering the mains power. That is, the short-circuit AC current through the capacitor prevents the interfering circuit from being connected to the outside.
Rectification measures for differential mode interference:
1. Increase the capacitance value of X capacitor
2. Increase the inductance of common mode inductance, utilize its leakage inductance, and suppress differential mode noise (because there are several winding methods for common mode inductance, such as double wire parallel winding or double wire separate winding, regardless of which winding method, due to loose winding, differences in wire length, etc., leakage phenomenon will definitely occur, that is, the magnetic field lines generated by one coil cannot completely pass through the other coil, which causes induced electromotive force between L-N lines, equivalent to connecting an inductor in series between L-N)
The following figure shows the common mode interference test FALL data:
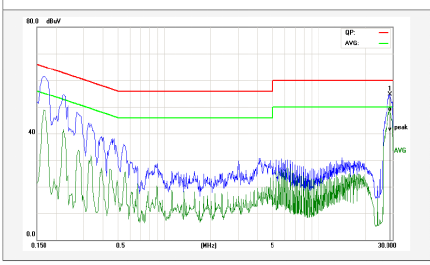
The parasitic capacitance between the power cable and the ground creates a loop for common mode interference, and the interference noise flows through this capacitance to the ground, forming a common mode interference current between the LISN cable parasitic capacitance ground, which is detected by the receiver and leads to conduction exceeding the standard (this can also explain why some motherboards pass through without grounding during conduction testing, and a ground wire exceeds the standard). In USB mode, when not grounded, the current loop can only pass through the L-diode load hot ground LED-N, and the common mode current cannot return to the LISN. The noise detected by the LISN is small, while when the cold ground of the motherboard is directly connected to the ground, there is a loop between the cable and the ground. At this time, if the common mode noise is not absorbed by the front-end LC filtering circuit, it will cause conduction exceeding the standard.)
Rectification measures for common mode interference:
1. Increase the common mode inductance
2. Adjust the LC filters on L-GND and N-GND to filter out common mode noise
3. The motherboard should be grounded as much as possible to reduce the impedance to ground, thereby reducing the parasitic capacitance between the cable and the ground.
2、 The sources of electromagnetic compatibility interference for the product include:
1. The switching circuit of the equipment switch power supply: the main frequency of the disturbance source ranges from tens of kHz to hundreds of kHz, and the high-order harmonics can extend to tens of MHz.
2. The rectification circuit of equipment DC power supply: the upper limit of the frequency of the power frequency rectification noise of the power frequency linear power supply can be extended to several hundred kHz; The upper frequency limit of high-frequency rectification noise in switching power supplies can be extended to tens of MHz.
3. Brush noise of DC motors in electric equipment: The upper limit of noise frequency can be extended to several hundred MHz.
4. The operating noise of AC motors in electric equipment: high-order harmonics can extend up to tens of MHz.
5. Disturbance emission of variable frequency speed regulation circuit: The frequency of the disturbance source in the switch speed regulation circuit ranges from tens of kHz to tens of MHz.
6. Switching noise during device operation: The upper frequency limit of noise generated by mechanical or electronic switch actions can extend to several hundred MHz.
7. Electromagnetic interference of crystal oscillators and digital circuits in intelligent control devices: The main frequency of the interference source ranges from tens of kHz to tens of MHz, and high-order harmonics can extend to hundreds of MHz.
8. Microwave leakage of microwave equipment: The main frequency of the disturbance source is GHz.
9. Electromagnetic disturbance emission of electromagnetic induction heating equipment: The main frequency of the disturbance source is several tens of kHz, and high-order harmonics can extend to several tens of MHz.
The local oscillator and its harmonics of the high-frequency tuning circuit of 10 TV electroacoustic receiving equipment: the main frequency of the disturbance source ranges from tens of MHz to hundreds of MHz, and the high-order harmonics can extend to several GHz.
11. Digital processing circuits for information technology equipment and various automatic control devices: The main frequency of the disturbance source ranges from tens of MHz to hundreds of MHz (with internal frequency doubling reaching several GHz), and high-order harmonics can extend to tens of GHz.

Advanced Institute (Shenzhen) Technology Co., Ltd, © two thousand and twenty-onewww.avanzado.cn. All rights reservedGuangdong ICP No. 2021051947-1 © two thousand and twenty-onewww.xianjinyuan.cn. All rights reservedGuangdong ICP No. 2021051947-2