

Hotline:0755-22277778
Tel:0755-22277778
Mobile:13826586185(Mr.Duan)
Fax:0755-22277776
E-mail:duanlian@xianjinyuan.cn
In the field of third-generation semiconductor substrate materials, Tianyue Advanced has entered the forefront of the industry. Faced with blockades and breakthroughs, the company's future development path is long and arduous.
On the last day of 2021, Huawei's rotating chairman Guo Ping delivered a New Year's speech and disclosed Huawei's somewhat helpless business situation in 2021. In 2021, Huawei's revenue was 634 billion yuan, a year-on-year decrease of 28.9%.
In 2020, the United States' upgraded regulation on Huawei chips officially came into effect, and TSMC stopped producing Kirin chips for Huawei. This move has dealt a heavy blow to Huawei's mobile phone business.
Nowadays, the top five mobile phone manufacturers no longer have Huawei's presence, and the once dominant Huawei phones are classified as "Others" in statistics, which is regrettable.
All of this stems from the inability of the domestic high-end semiconductor industry to achieve independent and controllable development. Without relevant technology, being choked by foreign countries is inevitable.
As a leading company in the domestic third-generation semiconductor silicon carbide substrate industry, Tianyue Advanced (688234) is about to land on the Science and Technology Innovation Board, enriching the domestic semiconductor industry.
Huawei's Hubble Investment's investment in 2019 tied up with domestic technology leaders, and the listing of Tianyue further attracted market attention.
Tianyue's main business belongs to third-generation semiconductors and is regarded as the "hope of the whole village". Against the backdrop of technology blockade and product embargo imposed by some developed countries on China, the future path of Tianyue is destined to be not smooth sailing.

Third generation semiconductors, a battleground for military strategists
Semiconductors have penetrated into every aspect of life. They are the core of electronic products, the cornerstone of the information industry, and also known as the "food" of modern industry. So what is a semiconductor?
Common semiconductor materials include elemental semiconductor materials such as silicon (Si) and germanium (Ge), as well as compound semiconductor materials such as gallium arsenide (GaAs), silicon carbide (SiC), and gallium nitride (GaN).
Broadly speaking, semiconductor refers to chips or devices made on semiconductor materials. Among them, silicon-based integrated circuits are the most common, and the well-known CPU and GPU chips belong to this category. Simply put, this type of chip is a miniaturized high-speed calculator made by printing circuits on a silicon wafer.
Currently, over 90% of semiconductor products are made from silicon-based materials, collectively referred to as the first generation semiconductors in the industry.
The first generation semiconductor started late in Chinese Mainland, which is far behind the international giants.
For example, TSMC and Samsung were already able to mass produce 5-nanometer process chips in 2021; However, SMIC, a leading domestic company, has a mature process of only 14 nanometers.
You should know that in 2016, high-end mobile phone chips had already reached a process of 14 nanometers. The seemingly small 10 nanometer gap is actually a huge intergenerational divide.
Although the country has strongly supported the development of the semiconductor industry in recent years and related industries have also experienced rapid growth, technological breakthroughs are not achieved overnight, and industry experience requires time to accumulate.
The backwardness of the first generation semiconductor process has led to domestic chip design manufacturers being at the mercy of others, and the sanction of Huawei mentioned earlier is a typical case.
However, hope always needs to be present.
With the popularization of intelligence, third-generation semiconductors have gradually found a suitable commercial positioning for themselves.
The third-generation semiconductor materials, represented by silicon carbide and gallium nitride, have many advantageous physical properties and are more suitable for high temperature, high voltage, and high frequency scenarios. For example, the fast charging heads of major mobile phone manufacturers rely on gallium nitride devices.
The first and third generation semiconductor materials have their own advantages and disadvantages, and there is no absolute substitution relationship, but rather their respective comparative advantages in specific application scenarios
Generally speaking, third-generation semiconductors are divided into two application branches: silicon carbide and gallium nitride. Both require a silicon carbide substrate, followed by epitaxial growth (depositing a layer of single crystal on the substrate). The difference lies in the fact that the silicon carbide substrates of the two are different, and their ultimate application directions are also different.
Gallium nitride needs to be deposited epitaxially on a semi insulating silicon carbide substrate. Silicon carbide needs to be obtained by depositing silicon carbide epitaxy on a conductive silicon carbide substrate.
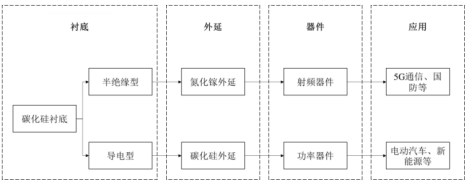
Source: Company prospectus
The third-generation semiconductor industry is currently in its early stages of development globally. Although international giants still lead domestic manufacturers in technology and experience, the overall technological gap between domestic and international giants is relatively small compared to the gap in first generation semiconductors.
In addition, due to the higher inclusiveness and tolerance of downstream processes in third-generation semiconductors, downstream manufacturing processes have relatively lower equipment requirements and relatively small investment amounts. The key constraint on industry development lies in the upstream material end (substrate).
Silicon carbide semiconductors will play an important role in new infrastructure fields such as 5G base station construction, ultra-high voltage, and new energy vehicle charging piles in the future. If a breakthrough can be achieved in the upstream substrate materials industry domestically, it is expected to overtake in the semiconductor industry.
The industry has high development certainty and high technological content, but the development of semi insulating silicon carbide substrates in China is very tortuous.
In 2008, the Wassenaar Agreement imposed clear restrictions on semi insulating silicon carbide substrate materials, and some developed Western countries, as members of the agreement, imposed strict sanctions on China, which restricted the development of the domestic semiconductor industry.
Especially with the recent impact of trade frictions, there is a clear downward trend in exports from US representative companies to China.
Taking the third-generation semiconductor leader CREE as an example, its sales to China in the 2019 fiscal year were $116 million, but decreased to $65 million in the 2020 fiscal year.
From this perspective, we can see that foreign semiconductor giants are banning the sale of high-end semiconductor related raw materials to China, attempting to contain the development of China's semiconductor industry.
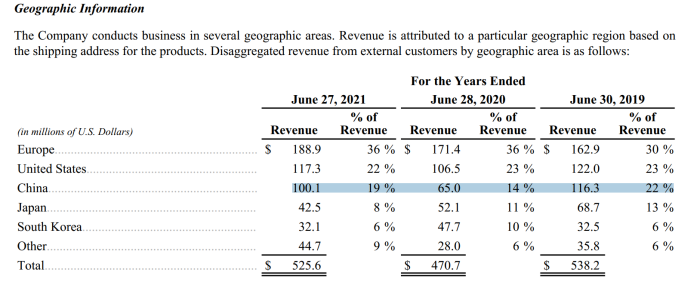
Source: Official website of Kerui Company
The 14th Five Year Plan has included silicon carbide semiconductors as a key support area and elevated it to a national strategy, highlighting the importance of third-generation semiconductors. In today's era where technology is king, this field has naturally become a global battleground.

Lack of market cross validation
Tianyue was founded in 2010, and its main business is third-generation semiconductor silicon carbide substrate materials, which belong to the upstream of third-generation semiconductors and provide raw materials for terminal RF or power devices. The company's main products include semi insulating and conductive silicon carbide substrates.
Before going public, the capital market had high expectations for it. However, upon closer inspection of Tianyue's business structure, there are still many areas of concern.
According to the prospectus, the revenue proportion of semi insulating substrate business is the highest, reaching 81.62% in 2020. Next is other income, with a relatively low proportion of conductive substrate business.
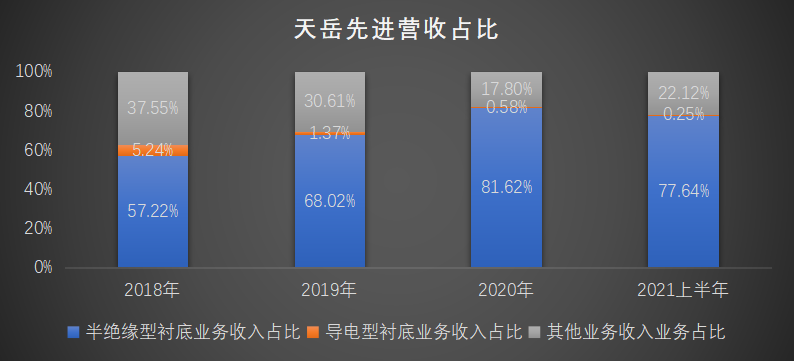
Source: Company prospectus, compiled by Alpha Workshop Research Institute
According to Yole's statistics, the market share of Tianyue's semi insulating silicon carbide substrates has increased from 18% in 2019 to 30% in 2020, ranking among the top three in the world in this market.
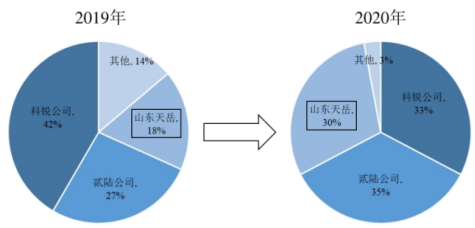
Source: Company Prospectus Yole
A significant increase in market share usually represents market recognition, symbolizing that the company's products have gained more customer recognition. However, Tianyue's customer concentration is much higher than its peers, which greatly reduces the value of its market share increase.
From 2018 to 2020, the total revenue contributed by the company's top five clients exceeded 80%, and in the first half of 2021, it reached an astonishing 91.68%, showing a trend of increasing concentration.
Especially the top two clients, who together contribute about 60% of the revenue, the company did not directly disclose their names, but only referred to them as client A and client B. According to other information in the prospectus, there are still traces of anonymous clients A and B.

Advanced Institute (Shenzhen) Technology Co., Ltd, © two thousand and twenty-onewww.avanzado.cn. All rights reservedGuangdong ICP No. 2021051947-1 © two thousand and twenty-onewww.xianjinyuan.cn. All rights reservedGuangdong ICP No. 2021051947-2